Japan Has Created the First Artificial Womb in the World
© freestockcenter / Freepik
Researchers in Japan are developing artificial womb technology, a groundbreaking innovation that could change how we care for premature infants and even reshape the future of childbirth.
This isn’t science fiction—it’s a reality scientists are working toward, and Japan is leading the way.
Let’s explore what this technology is, how it works, and what it means for the world.
What Is Artificial Womb Technology?
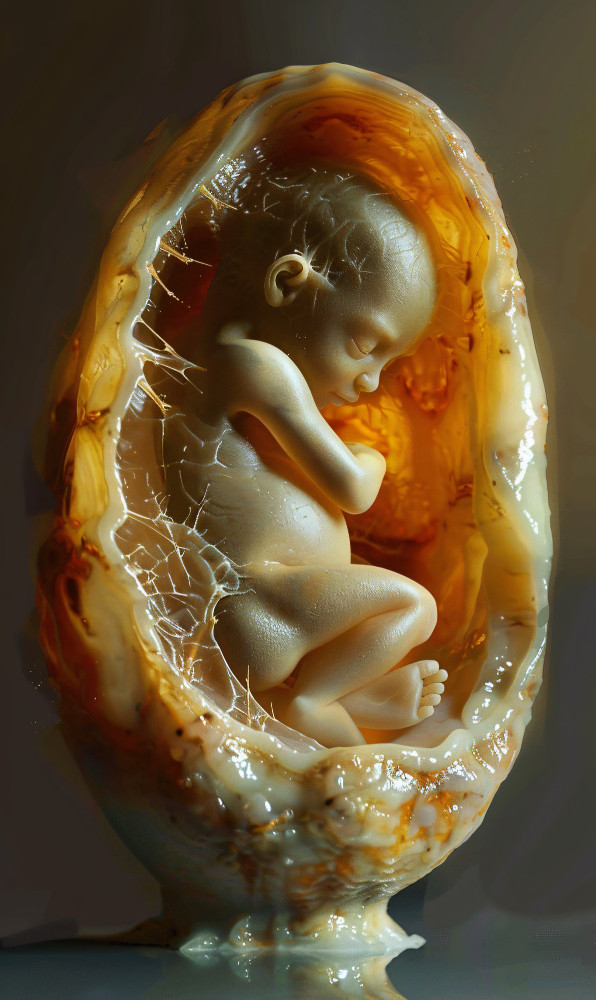
An artificial womb is a device designed to mimic the environment of a natural womb. It provides a safe, controlled space for a fetus to grow outside the mother’s body.
The system uses a fluid-filled chamber that acts like amniotic fluid, along with machines to supply oxygen and nutrients through the umbilical cord.
In Japan, scientists have tested this technology on animals like goats and sharks, successfully keeping embryos alive for weeks.
For example, researchers at Juntendo University sustained goat fetuses for up to three weeks in a plastic tank filled with artificial amniotic fluid.
This is a big step toward using the technology for human babies, especially those born extremely premature.
The goal is to help babies born before 37 weeks, who often face serious health risks.
According to the World Health Organization, 15 million babies are born prematurely each year, and 1 million die due to complications.
Artificial wombs could offer a lifeline by allowing these infants to continue developing in a womb-like environment, improving their chances of survival and healthy growth.
Japan’s Role in the Breakthrough

Japan has been a pioneer in this field for decades. As early as 1992, scientists at Tokyo University raised a goat fetus in a rubber womb for 17 days, a world first.
More recently, teams at Tohoku University and Kyushu University have pushed the technology further.
They’ve developed systems like the Ex-Vivo Uterine Environment (EVE) therapy, which has kept premature lamb fetuses alive for up to two weeks in a near-normal state.
These advancements show Japan’s commitment to solving real-world problems, like supporting premature infants and addressing population challenges through biotechnology.
Japan’s work isn’t just about saving lives. It also raises big questions about the future. For example, could this technology one day allow full pregnancies outside the body?
While that’s still far off, the progress made so far is exciting and full of potential.
Ethical and Social Impacts

Artificial womb technology is not without challenges. There are ethical concerns to consider. Who will have access to this technology?
If it’s expensive, will only the wealthy benefit? There’s also the question of how it might change the way we think about parenthood.
Some worry it could affect the bond between parents and babies or raise issues about consent and privacy.
For instance, could this technology be used without proper oversight? These are important questions that scientists and society must address as the technology develops.
Japan’s advancements could also have social benefits. For example, artificial wombs might help working parents or support same-sex couples and single individuals in starting families.
However, experts estimate it could take 10 to 15 years before the technology is ready for human use, and even then, it will need strict rules to ensure it’s used responsibly.
Looking Ahead

Japan’s work on artificial wombs is a game-changer for neonatal care. It offers hope for premature babies and opens the door to new possibilities in how we think about birth.
While there are still technical and ethical hurdles to overcome, the progress made so far is remarkable. As Japan continues to lead in this field, the world is watching closely.
This technology could save countless lives and change society in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
You might also want to read: A Woman With a Womb Transplant Gave Birth to a Perfectly Healthy Little Girl


