Alarming Stats: 1 in 3 U.S. Teens Have Prediabetes, Says CDC

© Freepik
Why is the teen prediabetes crisis a growing concern for public health?
This isn’t a distant future—it’s happening now. One in three teenagers is at risk of serious health problems before they even reach adulthood.
A recent report has raised alarms about the health of young people in the United States, pointing to a troubling trend that could affect millions of lives.
What’s behind this issue, and what can be done to turn things around?
A Shocking Rise in Prediabetes
A new study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows that nearly 1 in 3 U.S. teens aged 12 to 17—about 8.4 million adolescents—had prediabetes in 2023.
Prediabetes means blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
This condition increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Previous estimates suggested about 1 in 5 teens were affected, but the new numbers show a rise to 32.7%.
This increase is a wake-up call, as noted by Dr. Christopher Holliday, a CDC official, who called type 2 diabetes a “significant threat” to young people’s health.
The numbers are concerning, but experts point out that not every teen with prediabetes will develop diabetes.
Some of this rise may be linked to puberty, when hormonal changes can temporarily make teens more insulin-resistant. Still, the trend is clear: prediabetes is becoming more common, and it’s tied to rising rates of obesity and unhealthy lifestyles.
For example, kids with higher body mass index (BMI) or those facing challenges like poverty and food insecurity are at greater risk.
Why Is This Happening?
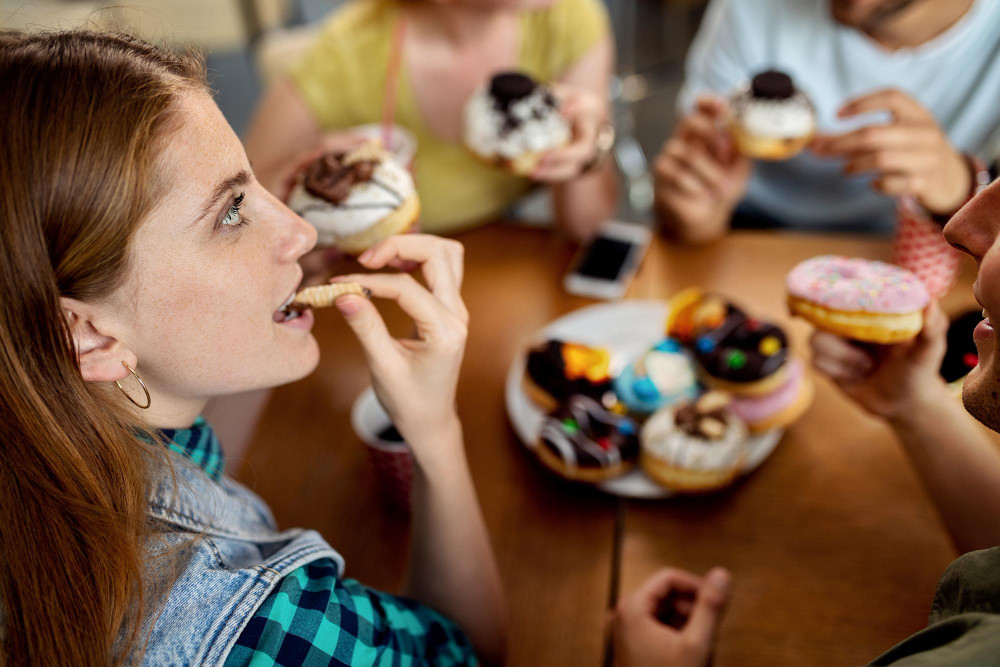

Several factors are driving the teen prediabetes crisis. Obesity is a major contributor, as extra weight can make it harder for the body to use insulin effectively.
The CDC notes that being overweight, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, or being physically inactive are key risk factors.
Research also shows that teens living in poverty or without access to healthy food and healthcare are more likely to have prediabetes.
For instance, a study in JAMA Pediatrics found that prediabetes rates among teens jumped from 12% in 1999–2002 to 28% in 2015–2018, with higher rates among those in lower-income households.
Lifestyle habits play a big role too. Diets high in sugary snacks and processed foods, combined with too much screen time and not enough exercise, are putting teens at risk.
Dr. Sonia Caprio, a pediatric endocrinologist, explains that even small changes, like eating more fruits and vegetables or getting regular exercise, can make a big difference in preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes.
Steps to Fight Back
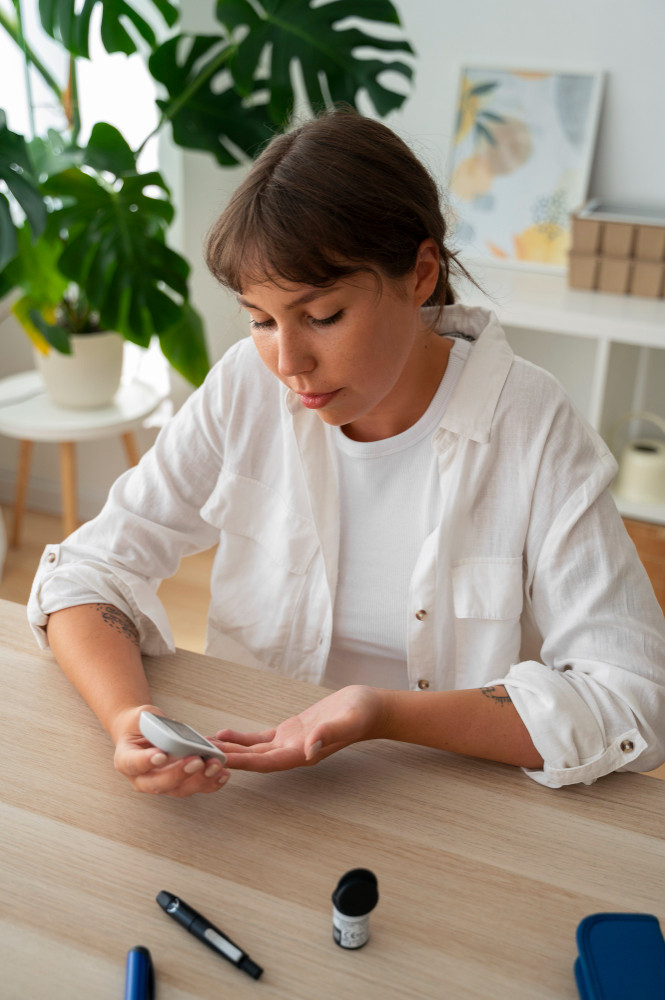

The good news is that prediabetes can often be reversed with simple lifestyle changes. The American Diabetes Association recommends that teens and families focus on healthy eating, such as choosing non-starchy vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains.
Regular physical activity, like 30 minutes of exercise most days, can help manage weight and improve blood sugar levels. For some teens, doctors may also suggest medications to help control blood sugar, but lifestyle changes are the first step.
Screening is another key tool. The American Diabetes Association advises testing for type 2 diabetes starting at age 10 for kids who are overweight or have other risk factors.
Catching prediabetes early gives teens a chance to make changes before it becomes a bigger problem. Parents, schools, and communities can also help by promoting healthier school lunches, encouraging physical activity, and ensuring access to nutritious foods.
The teen prediabetes crisis is a serious issue, but it’s not too late to act. By making small changes now, families can help protect the next generation from the risks of type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
This is a call to action for everyone—parents, teens, schools, and healthcare providers—to work together to build a healthier future.
You might also want to read: Diabetes Prevention 101: Breakfast Really IS Important


