Why Is Cashmere Fabric So Expensive?

Cashmere, a name synonymous with unparalleled softness and warmth, drapes itself not just around our bodies but also in a rich history and intricate production process.
This luxurious fabric, often referred to as “cashmere wool,” originates from the soft undercoat of goats native to the Gobi Desert and Kashmir region. Unlike its more common cousin, sheep’s wool, cashmere boasts a fineness and weightlessness that elevates it to the pinnacle of comfort.
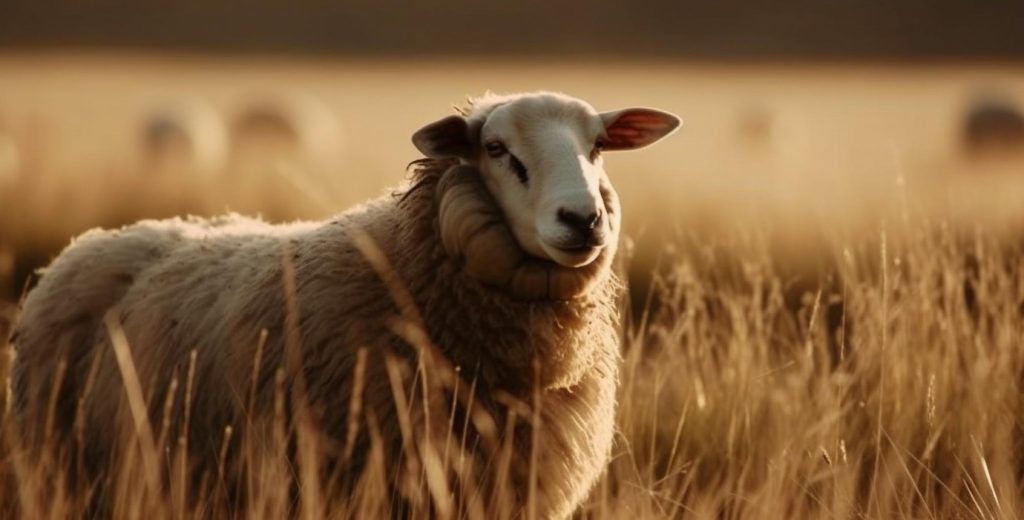

Unveiling the Distinction: Cashmere vs. Wool
While both wool and cashmere provide welcome warmth, understanding their key differences allows you to appreciate the unique qualities of cashmere:
- Source: The origin story of these fabrics starts at the farmyard. Cashmere comes from the gentle undercoat of cashmere goats, while wool is derived from the fleece of sheep.
- Softness: Cashmere fibers are significantly finer and softer than wool. Imagine the difference between a gentle touch and a warm hug – that’s the contrast between these materials against your skin.
- Warmth: Cashmere excels in providing exceptional insulation despite its lightweight nature. However, some types of wool, particularly those with a thicker fiber diameter, might offer slightly more warmth.
- Price: Due to its rarity and luxurious feel, cashmere commands a higher price point compared to wool.

A Timeless Tale: The History of Cashmere Fabric
Cashmere boasts a heritage that stretches back centuries, a testament to its enduring allure:
- Ancient Origins: Evidence suggests cashmere production existed as early as the 3rd century BC in Mongolia and the Kashmir region. Imagine nomadic herders crafting garments from this precious fiber long before the modern world.
- European Arrival: Cashmere’s exquisite qualities eventually reached Europe through established trade routes. Its luxurious touch captivated nobility, solidifying its association with opulence and sophistication.
- Modern Production: Today, China is the leading producer of cashmere, leveraging large-scale facilities. However, traditional cottage-style production persists in Central Asia, where the practice remains deeply rooted in the cultural fabric of the region.
From Goat to Garment: The Production Journey of Cashmere
Cashmere fabric undergoes a meticulous process before gracing your wardrobe:
- Shearing: The soft undercoat of cashmere goats is gently shorn, ensuring minimal discomfort to the animals.
- Cleaning: Raw cashmere undergoes a meticulous cleaning process to remove dirt and impurities, preparing the fibers for their transformation.
- Combing and Carding: Individual fibers are straightened and aligned using specialized tools. Imagine combing out tangles but on a much larger scale.
- Spinning: The aligned fibers are then spun into fine yarn, creating the building blocks for the future garment.
- Finishing Touches: Depending on the desired outcome, the yarn might be dyed, cleaned again, and treated for various purposes like wrinkle resistance or flame retardancy.
- Weaving: The finished yarn is woven into luxurious garments like scarves, sweaters, and even delicate undergarments.

Cashmere Fabric: Beyond Luxury, Towards Ethical Fashion
Cashmere’s luxurious qualities make it ideal for various clothing applications:
- Soft and Delicate: Cashmere’s delicate nature makes it perfect for lightweight garments like sweaters, scarves, and cozy hats. The fabric’s exceptional warmth-to-weight ratio allows for luxurious pieces that don’t weigh you down.
- Formal Wear Legacy: Cashmere’s association with luxury endures, making it suitable for sophisticated clothing. Imagine the timeless elegance of a cashmere coat or the soft touch of a cashmere dress.
- Ethical Considerations: When choosing cashmere, opting for ethically sourced options ensures responsible treatment of the goats. Look for certifications that promote sustainable practices and animal welfare.
Cashmere Fabric’s Environmental Impact: A Balanced View
Cashmere’s environmental impact presents a complex picture, with both positive and negative aspects to consider:
- Positive Aspects: Cashmere is a natural and biodegradable fiber, unlike synthetic alternatives that pollute the environment for years. Additionally, unlike cotton, wool production, including cashmere, doesn’t require harsh pesticides or fertilizers.
- Sustainability Concerns: Unethical cashmere production practices can harm the environment. Overgrazing by cashmere goats can lead to desertification if not managed responsibly. Thankfully, certifications like the Sustainable Cashmere Standard and Recycled Claim Standard are taking strides to promote ethical and sustainable cashmere production.

By understanding the unique properties, history, and production process of cashmere fabric, you can appreciate its luxurious qualities while making informed choices for your wardrobe. Look for ethically sourced cashmere and embrace the feeling of a fabric steeped in history and crafted with nature’s finest fibers.
You might also like to read: What Is Fast Fashion and How Does It Impact the World